Architecture
ARO Network constructs its edge cloud infrastructure using a three-layer architecture model:
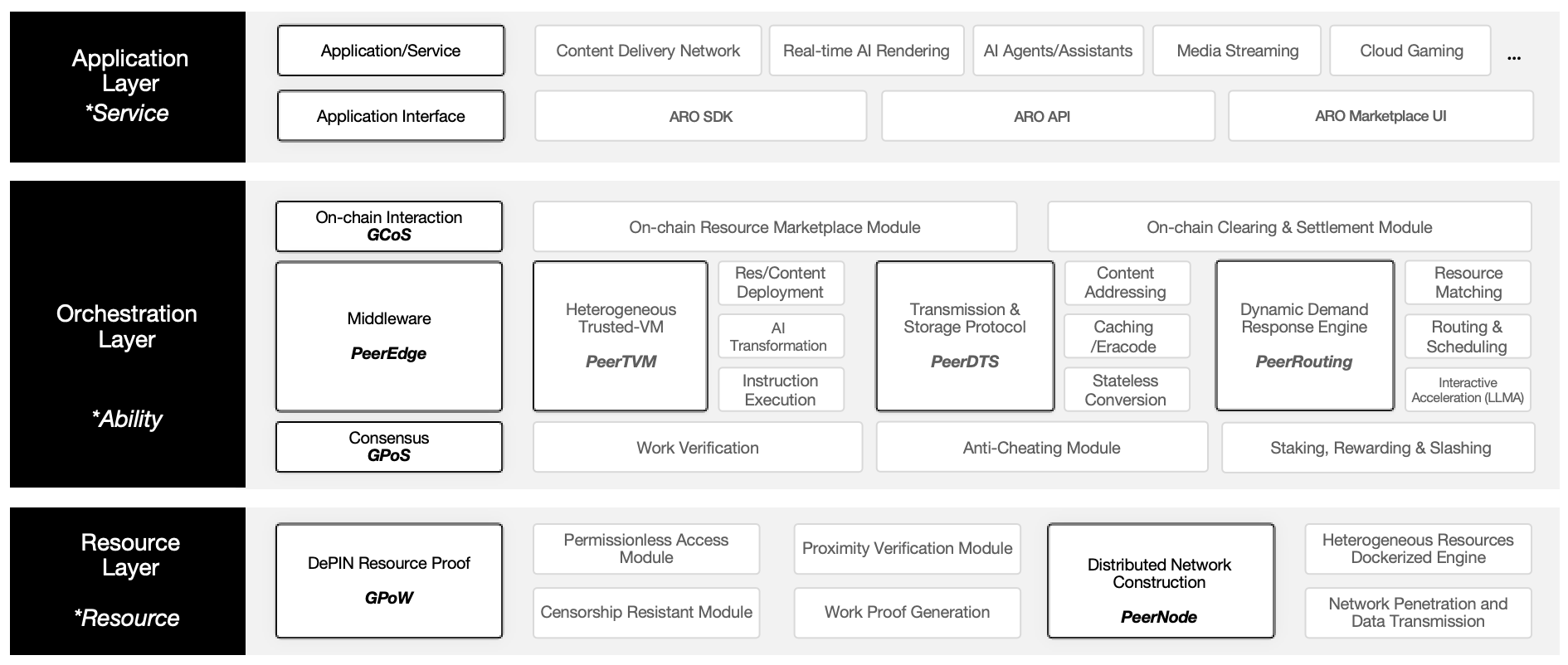
Resource Layer
This is the foundational layer of ARO, consisting of a vast, distributed, and permissionless network of hardware resources. These resources provide the bandwidth, storage, and computing power that underpin the edge cloud.
At this layer, we focus on solving two fundamental challenges:
-
Trust:
How can large-scale distributed nodes verify one another and trust the results of such verification? -
Functionality:
In a network with high node heterogeneity, how can we effectively virtualize and containerize these nodes while establishing a P2P transmission network that can penetrate firewalls and local networks?
Open Layer
This is where ARO actively orchestrates network resources to optimize the match between supply and user demand.
At the base of this layer lies a trust mechanism for verifying node workloads. On top of this, we introduce a capability abstraction engine known as the PeerEdge Middleware.
PeerEdge consists of three core components:
-
PeerHVM (Peer Heterogeneous Virtual Machine)
Abstracts P2P network resources to provide standardized capability outputs. With PeerHVM, ARO can deploy capabilities across distributed nodes to form a unified and interoperable network structure. -
PeerDTS
A high-performance P2P transmission protocol that enables large-scale content delivery across the capability layer abstracted by PeerHVM. -
PeerRouting
A dynamic, preemptive response engine that intelligently matches resources to continuously changing user demand.
Application Layer
Leveraging the capabilities provided by the middleware and the corresponding on-chain interfaces, this layer offers user-facing interfaces, service components, and application APIs for CDN, cloud storage, AI inference, runtime transmission, and compute routing services provided by third parties.
As part of our phased approach, this layer is open to the developer community to foster a wide range of applications—fulfilling ARO’s vision of Universal Acceleration.
Resource, Trust, and Service
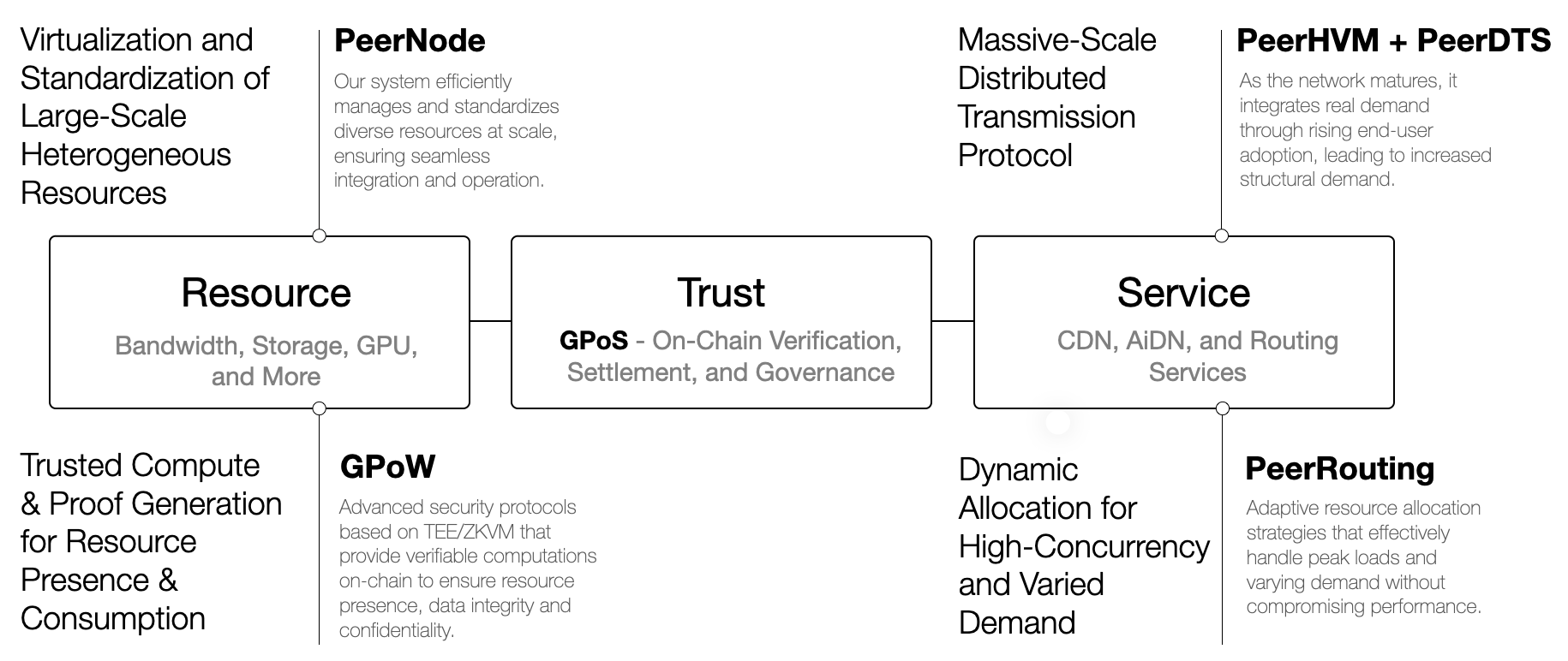
The Resource–Trust–Service model provides a clear, modular abstraction for how ARO organizes edge hardware into a robust edge cloud network, highlighting the key technologies involved.
-
The Resource layer focuses on virtualizing and standardizing the large-scale, heterogeneous PeerNode resources to provide decentralized computing capabilities. It uses the GPoW (Guarantee Proof of Work) protocol to offer trustworthy, verifiable work proofs.
-
The Trust layer employs the GPoS (Guarantee Proof of Stake) protocol to ensure trusted on-chain verification, settlement, and governance of these work proofs.
-
The Service layer leverages the PeerHVM, PeerDTS, and PeerRouting middleware to deliver services such as CDN, AiDN, and routing based on these verifiable PeerNodes.
By integrating these technologies, ARO creates a high-performance, cost-efficient AI acceleration network grounded in industry best practices.